Plantain
11 min read
Plantain is a grazing herb that grows well across New Zealand. Plantain is compatible with other pasture species and can be managed on a similar rotation length as perennial ryegrass, making it a good fit for most farm systems. Research shows Ecotain™ plantain can help farmers reduce their environmental footprint by decreasing nitrogen losses without requiring major changes to their farm systems or management. Plantain case studies provide examples of different ways farmers are incorporating plantain into their farm systems as a low-cost way to reduce nitrogen leaching.
Plantain is a herb with a fibrous and coarse root system that grows throughout New Zealand and is highly palatable to animals. Plantain is one of the few species that can be managed on a similar rotation length as perennial ryegrass, making it a good fit for the majority of farm mixes. There are two ways to grow plantain: as a pasture mix or as a special purpose crop.

Trials conducted through the Plantain Potency and Practice Programme show that plantain is a low cost, moderate impact tool for reducing nitrate leaching. Research through the New Zealand Agricultural Greenhouse Gas Research Centre (NZAGRC) is showing that in some cases plantain can significantly reduce nitrous oxide emissions but results to date have been variable.
The biggest contributor to nitrate leaching and nitrous oxide emissions from dairy farms is the urine patch. Urea in urine is converted to ammonia (hydrolysis) and then to nitrate (nitrification) by soil microbes.
Ammonia and nitrate are taken up by plants, however the nitrogen concentration is too great for plants to use. Excess nitrate dissolves easily and can leach below the root zone and move to surface or ground water. Excess nitrate can be further converted to nitrous oxide gas by different soil microbes. Nitrous oxide is a potent and long-lived greenhouse gas. There are five ways Ecotain™ plantain reduces nitrogen loss.
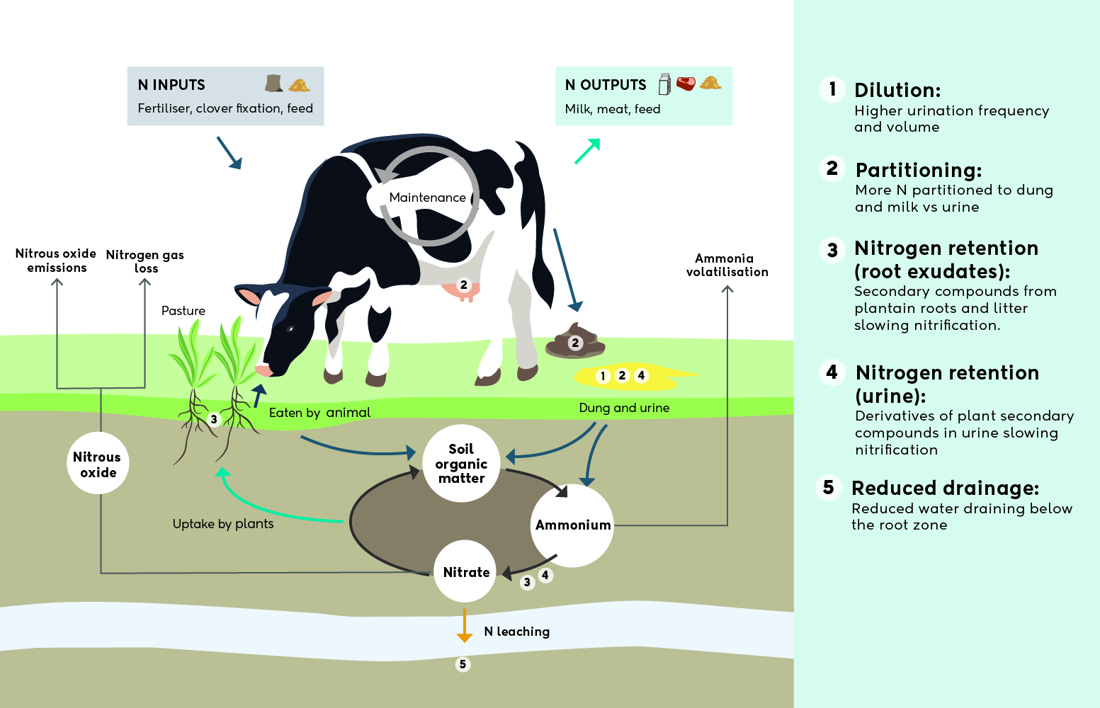
A depiction of the nitrogen cycle
When Ecotain™ plantain is included in the diet, the number of urination events and total urine volume increase, and consequently the urinary nitrogen concentration in each urine patch decreases.
The reason for the increase in urine volume is, at least in part, due to increased water consumption. Ecotain™ has on average around 30% lower dry matter content than perennial ryegrass1. Urine volume increases proportionally with the amount of Ecotain™ in the diet2.
There may be other factors contributing to the dilution effect of plantain and are being investigated as part of the Plantain Potency and Practice Programme.
Nitrogen consumed by cows is partitioned to body mass, milk, faeces, and urine.
The portions of nitrogen in each output depend on the diet. When Ecotain™ plantain is included in a cow’s diet, the portion of nitrogen intake partitioned to urine decreases, and the portion partitioned to faeces and milk increases when compared to perennial ryegrass2,3. The reason for this difference can be explained by the nutritional components of the plant:
Plant secondary compounds found in Ecotain™ also contribute to reducing ammonia production in the rumen4 and may further reduce N excreted in urine.
The Plantain Potency and Practice programme is working to understand more about these processes and how they contribute to reducing N loss.
Ecotain™ plantain can reduce nitrate leaching and nitrous oxide emissions through changes to soil processes. Different pathways for reducing nitrate leaching and nitrous oxide emissions include:
The roots: The roots of plantain release plant secondary compounds which may restrict nitrifying bacteria and slow the accumulation of nitrate, giving pasture more time to use the nitrogen before it is lost.
The leaf: Plant secondary compounds in the leaf of the plant are eaten by animals, broken down further and their end-products are excreted in urine. There is evidence of these compounds restricting nitrifying bacteria and slowing nitrification.
Drainage: Plantain has reduced the amount of water drainage in several lysimeter experiments. This may contribute to reduced N leaching.
Note: Early research findings indicate that the effectiveness of the soil mechanisms vary with soil type and climate.
The well-demonstrated urinary nitrogen mechanisms (urine dilution and changes to animal partitioning) are now in the OverseerFM model. The Plantain Potency and Practice programme aims to improve understanding of the soil mechanisms and how they work in different soils and climates, so these effects can be included in the model.
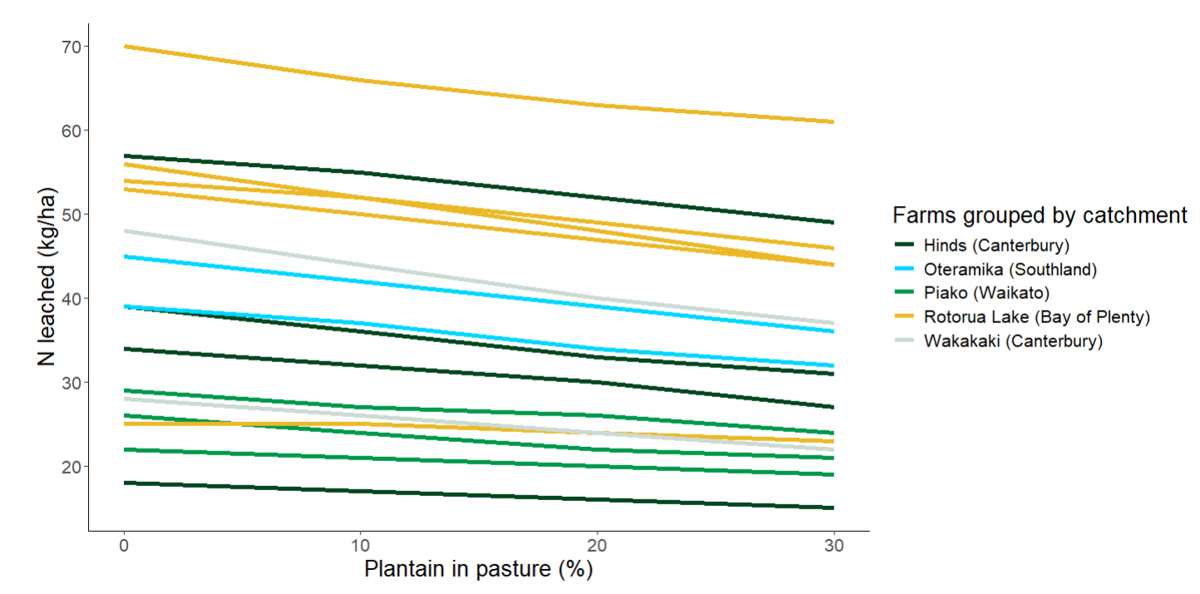
When modelled in OverseerFM, the reduction in whole-farm nitrate leaching from using plantain is relative to the amount of plantain on the farm. For example, for 12 of the partner farms, there was an average 6% reduction (range 3-8%) in nitrate leaching for every 10% plantain on the farm when modelled in OverseerFM. The estimated reductions in nitrate leached for the different catchments are shown below.
The amount of plantain in pasture is not necessarily representative of the amount of plantain in the diet, as this is influenced by the level of supplementary feeding.
Plantain is now recognised as a nitrogen leaching mitigation option by regional councils in Canterbury, Horizons, Waikato, Southland and Bay of Plenty, where N leaching limits are in place. For more information on how to get credit for using plantain to meet nutrient limits, contact your regional council or read here for Environment Canterbury.
The percentage of plantain on farm is important. Measure how much is present on your farm using the plantain Visual Assessment Guide and the Plantain Cultivar Evaluation System.
Nitrous oxide: NZAGRC-funded research is studying plantain’s potential to reduce the greenhouse gas nitrous oxide (N2O). Other work to date has shown reductions in the urine patch up to 50% with 30% plantain in the sward (Agritonic cultivar)5 but other studies have shown variable results6,7. These differences could be due to soil or climate, and further work is needed to understand the variability in results.
Methane: One study8 showed that total methane emission increased in heifers fed diets including plantain, because feed intake increased. Methane production per unit of dry matter eaten was reduced by 30% with 45% plantain in the diet.
In another study9, methane emissions per unit of dry matter intake were lower for cows fed 100% plantain compared to ryegrass. In this experiment this was due to plantain having a lower digestibility than ryegrass in this experiment.

Plantain offers potential yields of 10-19 t DM/ha/year. Despite the moderate drought tolerance, plantain still requires moisture to grow well. Under severe drought, plants will wilt, and yield will be reduced. However, it is often one of the first species to recover following rain, irrigation or effluent application.
Annual pasture yield and feed quality (metabolisable energy and crude protein) in plantain mixed swards is similar to perennial ryegrass/clover swards. A dry matter yield benefit in plantain mixed swards is often seen in summer and autumn.
Pure swards generally have lower winter and early spring growth rates than perennial ryegrass/clover.
Plantain is highly palatable and is often preferred by cows when grazing. Plantain can become less palatable when in the seed head stage, or if the plants have low nitrogen levels. Palatability can also reduce when grazing rounds become too long and plantain leaves aren’t grazed, leading to old leaves with low nutritional value. Old leaves can also attract disease and shorten the plant’s lifespan.
To select a plantain cultivar that is proven to reduce nitrogen loss, refer to Evaluating Plantain Cultivars.
To date, almost all published evidence for plantain’s ability to reduce nitrate leaching has used Ceres Tonic or Agritonic plantain cultivars. Ceres Tonic is no longer commercially available and Agritonic is marketed by Agricom as Ecotain™. There is evidence of variation between different cultivars for some of the drivers of reductions in N leaching.
There are three ways to establish plantain on farm:
New pastures
Adding plantain seed to new pasture mixes as part of your re-grassing programme is an easy way to incorporate plantain on farm. Plantain should be included in the seed mix at 3-4 kg seed/ha and sown no deeper than 10 mm.
There are limited options for broadleaf weed control in plantain pastures. Good weed control before establishment is critical to success. Some farmers have established their grass first, then controlled broadleaf weeds before broadcasting or undersowing with plantain and clover.
Pure crops
Pure plantain crops are suitable for short rotations or as a break crop in pasture renovations. When establishing, apply herbicide to existing pasture and direct drill the plantain seed following cultivation or minimum tillage (where applicable). Plantain seed should be sown at 10-12 kg/ha, with up to 5 kg/ha of clover seed.
Pure swards of plantain require nitrogen fertiliser application if they are not sown with clover. Sowing with clover restricts the weed control options available.
It is important to watch for bloat in plantain/clover swards. Farmers often graze pure plantain crops on-off with ryegrass pastures.
Pure plantain swards with clover levels above 20% may increase the risk of N loss due to N fixation and high protein content of the clover. In crops with very high clover, over-sowing with grass will reduce this risk.
Plantain can be incorporated into existing pastures as a low-cost and easy way to introduce plantain or maintain plantain in pastures over time.
Broadcasting: Plantain can be broadcast on existing pastures with fertiliser or using a tow-behind spreader at a rate of 2-5 kg/ha. Prillcote (lime coating) will help throw the seed evenly. If seed is coated, then the sowing rate (kg/ha) should be doubled. Establishment using broadcasting can be slow. If broadcasting in spring, plants can be expected to emerge in the following autumn.
Farmers have been able to achieve up to 20% plantain across the farm by establishing all new pastures as plantain mixed swards, and maintaining plantain presence with broadcasting. Farms in the Waikato and Bay of Plenty, and on stoney soils in Canterbury have seen the greatest success with broadcasting, where pastures are more open.
Undersowing: Plantain can be undersown into existing pastures at 4 kg/ha. Direct drill into low pasture cover (after hard grazing or mowing) and graze early after sowing while seedlings are still small to avoid defoliation. Both undersowing and broadcasting can be used in damaged pastures or pastures with gaps.
Plantain is more sensitive to sowing depth and soil temperature than ryegrass. The recommended sowing depth is no greater than 10 mm due to the small seed size, and it establishes best in warm soils (10-12oC).
Sowing in spring, after frosts and before summer dry conditions begin will ensure plants develop quickly. Plantain can be sown in early autumn before soil temperatures start falling, although establishment may be slower.
Plantain can be grown on a range of soils, although persistence is generally lower on heavy clay soils prone to waterlogging. Plantain may be outcompeted within one or two years in productive ryegrass pastures, or not establish well at all.
Soil fertility is important to achieve optimum growth. Seek advice on this from your soil nutrient advisor.
Plantain can be managed on a similar grazing rotation length as perennial ryegrass, making it a good fit for most farms.
Growth rates: Growth rates of plantain between spring and autumn range between 25 and 80kg DM/ha/day, potentially peaking at 140kg DM/ha/day in summer. Growth rates during winter are lower (15-35kg DM/ha/day). This can be dependent on cultivar selection.
Mixed swards: Ensure plantain is not outcompeted by ryegrass in new pastures. An early, light grazing is recommended; once the ryegrass passes the pluck test (lightly pull the grass to ensure the roots won’t be lifted when grazed) and plantain seedlings are below grazing height. The second grazing must occur after the six-leaf stage for plantain, that is, the plants have six fully grown leaves, to ensure plants have well-developed root systems.
Pure crops: Pure plantain crops should not be grazed before they reach the six-leaf stage. In spring, this is normally 7-8 weeks after sowing, and may be later in autumn.
Mixed swards: are best grazed at a leaf height of 25 cm (around 4-6 weeks of regrowth), or 2500-3300 kg DM/ha. The pre-grazing height is especially important in second year crops (spring sown, or the first year after autumn sowing) to reduce plantain seedhead and maintain feed quality.
Pure crops: are best grazed between 25-35 cm height.
Note: Cover heights are measured by leaf height ignoring the stems.
Plant density: In pure crops can impact apparent grazing mass. A high density first-year plantain crop (approximately 180 plants/m2) at a height of 25 cm can have a pre-grazing mass of around 3300 kg DM/ha. A less dense crop (approximately 80 plants/m2) at a height of 25 cm can have a pre-grazing mass of around 2300 kg DM/ha.
A rising plate meter (RPM) can estimate plantain crop yields. The Plantain Potency and Practice programme showed that at plantain levels less than 30%, the same RPM equation as ryegrass/white clover can be used. A different RPM equation is needed when there is a higher percentage of plantain, as plantain has a lower dry matter content than ryegrass. More work is underway to develop guidance on this.
Plantain is a short-lived plant, with a lifespan shorter than perennial ryegrass or white clover. In grass-dominant pastures, it reaches peak abundance 12 to 18 months after sowing and usually declines after two to three years.
Annual maintenance applications of phosphate, sulphur and potassium are needed for plantain – the same as ryegrass. Plantain responds very well to nitrogen fertiliser, even during summer.
Programme partner farmers are having success with regular broadcasting of plantain seed with fertiliser to maintain adequate levels in pastures. In pure crops, weed invasion is often seen after 18 months.
To achieve maximum longevity and yield with a pure plantain crop it’s important to focus on:
Eliminate weeds before sowing plantain. Plantain is sensitive to residual herbicides that may be used before sowing, so stick to the withholding periods. There are few suitable post-establishment herbicide options for plantain in mixed pasture swards. Speak to your agronomist for advice.
In late February to mid-March, holes may begin to appear in plantain leaves. These are caused by caterpillars (e.g., plantain moth, white butterfly, diamondback/cabbage moth). As caterpillars don’t feed on roots or growing points, this doesn’t usually affect plant growth. If the damage is severe, caterpillars can be controlled with an approved insecticide.
Plantain moth can be an issue in pure plantain crops, or mixed swards with a high proportion of plantain.It can be sprayed with a broad-spectrum insecticide at the larval stage, from December to May.
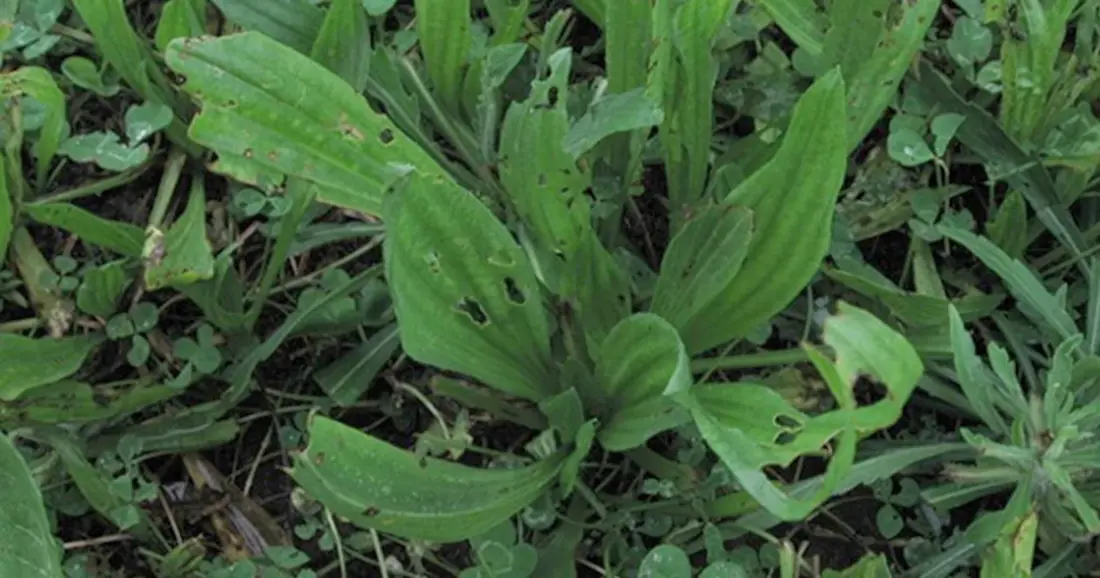
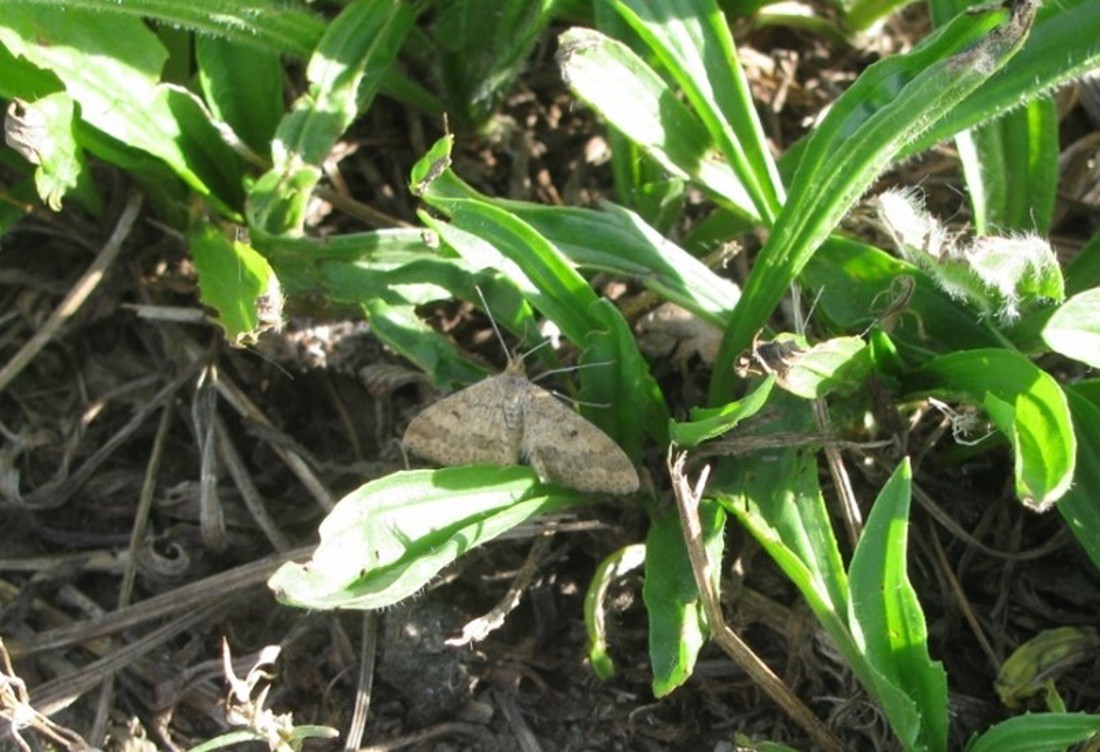
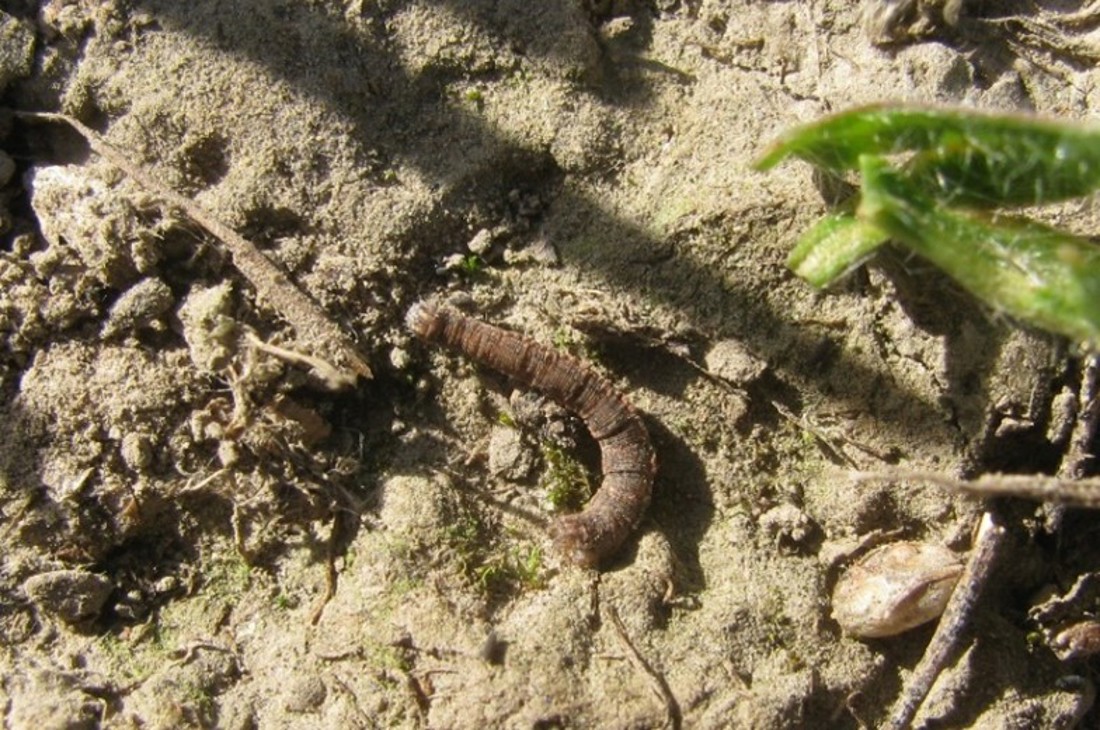



Based on data collected to date, plantain pastures appear to have lower facial eczema spores than perennial ryegrass pastures.

Graze cows on a consistent diet during calving, rather than changing between pastures with and without plantain. This is due to differences in calcium, magnesium, potassium and sodium content.
Animals drink less water while grazing plantain due to the high-water content of the feed. This may reduce intake of minerals or other medication supplied via inline water dispensers.
Cows grazing pastures with a high proportion of plantain may have increased risk of bloat, particularly where white clover intake is high.
In the same soil, plantain takes up more copper than perennial ryegrass/white clover pastures. The copper in plantain may be more bioavailable to the animal which increases liver copper stores and may result in copper toxicity. Monitor cow liver copper concentrations and discuss your copper supplementation strategy with your vet.
References
1 Minnée EMK, Kuhn-Sherlock B, Pinxterhuis IJB, Chapman DF. 2019. Meta-analysis comparing nutritional composition of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) and plantain (Plantago lanceolata) pastures. Journal of New Zealand Grasslands 81, 117-124.
2 Minnée EMK, Leach CMT, Dalley DE (2020) Substituting a pasture-based diet with plantain (Plantago lanceolata) reduces nitrogen excreted in urine from dairy cows in late lactation. Livestock Science.
3 Marshall CJ, Beck MR, Garrett K, Barrell G, Al-Marashdeh O, Gregorini P. 2021. Nitrogen balance of dairy cows divergent for milk urea nitrogen consuming either plantain or perennial ryegrass. Animals 11, 2464.
4 Navarrete S, Kemp PD, Pain SJ, Back PJ. 2016. Bioactive compounds, aucubin and acteoside, in plantain (Plantago lanceolata L.) and their effect on in vitro rumen fermentation. Animal Feed Science and Technology 222, 158-167.
5 Simon PL, de Klein CAM, Worth W, Rutherford AG, Kieckow J. 2019. The efficacy of Plantago lanceolata for mitigating nitrous oxide emissions from cattle urine patches. Science of the Total Environment 691, 430-441.
6 Podolyan A, Di HJ, Cameron KC. 2020. Effect of plantain on nitrous oxide emissions and soil nitrification rate in pasture soil under a simulated urine patch in Canterbury, New Zealand. Journal of Soils and Sediments 20, 1468-1479.
7 Rodriguez MJ, Kemp PD, Bishop P, Hanly JA, Navarrete SH, Horne DJ. 2020. Plantain sward: is it effective in reducing N2O emissions in spring and autumn? Farmed Landscapes Research Centre, Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealand, 10 p. http://flrc.massey.ac.nz/publications.html.
8 Minnée E, Dalley D, Bryant M, Leach C, Bagley E. 2018. The effect of plantain in the diet of dairy cattle on methane yields and nitrogen excretion. Report prepared for NZAGRC-PGgRc. Available on request.
9 Della Rosa MM, Sandoval E, Luo D, Pacheco D, Jonker A. 2022. Effect of feeding fresh forage plantain (Plantago lancelolata) or ryegrass-based pasture on methane emissions, total-tract digestibility, and rumen fermentation on nonlactating dairy cows. Journal of Dairy Science 105.
Now’s the perfect time to check in, plan, and set up for a strong season. We’ve pulled together smart tips and tools to help you stay ahead all winter long.
Whether you prefer to read, listen, or download handy guides, we’ve got you covered with trusted tools to support your journey every step of the way.